Intraoperative Neurophysiology
Neurotoc minimizes the risk of nervous system complications during brain, spinal cord, and nerve surgeries.
What is IONM?
Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring (IONM) is a medical technique used during surgical procedures to monitor the functioning of the patient’s nervous system in real time. Its main objective is to prevent neurological damage while performing procedures in delicate areas, such as the brain, spinal cord, or peripheral nerves.
How does it work?
During surgery, electrodes are used to record the electrical activity of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles. This allows the medical team to quickly detect any abnormalities or risk of injury and adjust their surgical approach if necessary.
What is being monitored?
Depending on the type of surgery, different neurophysiological signals can be monitored:
Somatosensory evoked potentials (SSEPs): assess sensation.
Motor evoked potentials (MEPs): assess motor function.
Electromyography (EMG): measures the electrical activity of muscles.
Electroencephalogram (EEG): monitors brain activity.
Auditory, visual, and other potentials are used in specific surgeries.
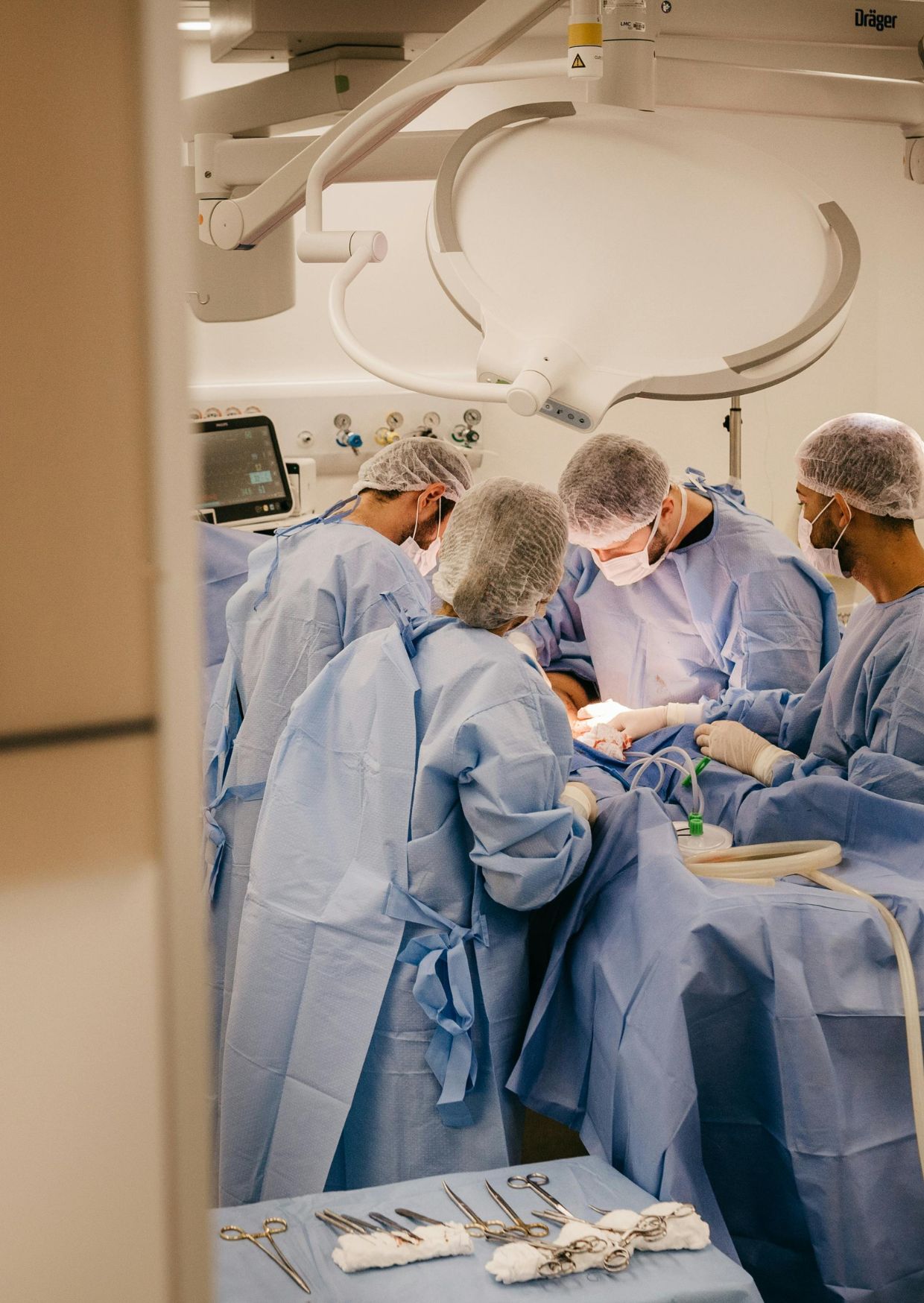
Services
It is common in operations such as:
- Spinal surgeries: herniated discs, lumbar fusion, scoliosis, fractures…
- Neurosurgery: brain or spinal cord tumors
- Vascular surgeries near the nervous system
- General surgery: thyroidectomy, parotidectomy
- ENT: tympanoplasty, cholesteatoma
- Hip surgeries
Do you want to train with us?
Main benefits
It reduces the risk of neurological sequelae (paralysis, loss of sensation, etc.).
It allows for an immediate response to signs of neurological damage.
It improves patient safety during complex procedures.
Leaders in Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring
Since our founding in 2011, at Neurotoc we have consolidated our position as a benchmark in Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring (IONM), collaborating with more than 40 clinics and hospitals throughout Spain.
The use of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring allows:
Reduce hospitalization and recovery time, improving healthcare efficiency.
Prevent irreversible neurological damage by detecting alterations in real time.
Optimize surgical outcomes in high-precision procedures.
Reduce the risk of postoperative neurological deficits and long-term complications.
